Energy Storage Industry
What is Energy Storage?
As renewable energy use grows, energy storage is becoming increasingly important due to the fluctuations which occur during renewable energy production but also as a way of obtaining higher revenues during peak times.
Energy storage can be in the form of many different technologies of which batteries are the most common but other technologies include pumped hydro, chemical storage, Compressed Air (CAES) thermal storage or within electric capacitors or electromagnets.
What are the ways in which Energy can be Stored?
Pumped Hydro
This is where during times of low energy cost or high availability of energy water is pumped to a higher reservoir. During times of high energy cost water is then allowed to flow back to a lower reservoir through a turbine or pump as a turbine generating electricity. Such schemes can be open-loop which is from naturally occurring changes in height to closed-loop projects were the reservoirs are artificially created.
Compressed Air Energy Storage
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) systems utilise excess electricity to compress air via an air compressor and store the air underground.
The air is then heated, causing it to expand which is used to drive a turbine producing electricity. The air can be stored in underground caverns which may have previously contained oil, gas or salt.
The two types of plant available are Diabatic and Adiabatic. Diabatic plants operate similar to Gas Power Stations but with compression and combustion processes separated producing 3 times more energy than a conventional turbine, but have a maximum efficiency of 60% and result in green house gas emissions. Adiabatic plants store thermal energy which is used to heat the compressed air during generation stages enabling plant efficiencies of 70% or higher.
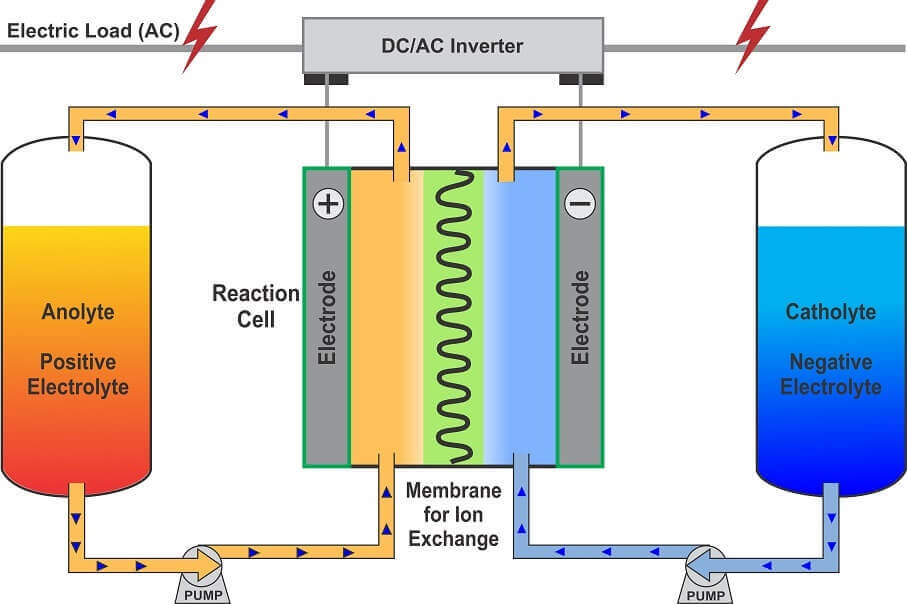
Redox Flow Battery
Redox flow batteries store energy within two solutions containing an electrolyte which are pumped into a tank consisting of a twin-chamber where the fluids react and ion exchange occurs. The liquids used within this process are anolyte (positive electrolyte) and catholyte (negative electrolyte). Hybrid systems consist of 1 electrolyte and solid metal. Current Redox flow batteries consist of Vanadium redox for flow batteries but brine can also be used. In hybrid systems, the most common fluid used is zinc-bromine.
Hydrogen / Chemical Storage
Chemical storage of energy is possible through the use of using excess energy to electrolyse water, creating hydrogen and oxygen which can be combusted within a turbine to create electricity.
As hydrogen production requires large amounts of electricity (electrolysis) to split hydrogen atoms from water, Hydrogen production can be created cost effectively via the utilisation of excess electricity.
The process of Electrolysis has a low efficiency ranging between 30-40% meaning generation is expensive. Hydrogen storage is currently under developed, however projects are being undertaken to hydrogenate hydrogen by combining it with a chemical such as Benzene, Dibenzyltoulene (DBT), Napthalene, toluene or a derivative to absorb the hydrogen molecules into their structure.
This makes handling safer and easier to handle. This liquid is then referred to as a Liquid Organic Hydrogen Carrier or LOHC.
Li-ion batteries
Lithium batteries act as a storage of electricity with the battery being constructed of Lithium metal, an insulator and another metal which may be cobalt, manganese, or iron phosphate. Some batteries incorporate a full battery management system (BMS) to ensure equal cell loading, prevent overcharging and ensure temperatures are maintained through glycol cooling. Such storage is currently used within houses, cars, and devices such as power tools. Their lifespan is limited to approximately 1000-3000 cycles.
Aqueous Sulphur Flow
Aqueous Sulphur flow battery utilises a sulphur cathode, oxygen, water and salt as a way of producing a relatively cheap solution where space is not an issue with low energy density.
Thermal Storage
Thermal storage of energy is a way of utilising heat to store energy by converting water to steam or utilising the heat during heating. Examples include storing of solar energy into molten salt for heating of water to create steam or electric storage heaters which contain ceramic which stores heat overnight in homes.
Whatever your process within energy storage we can provide pumps engineered with the following features to assist in your application:
Pumps as turbines to generate electricity from excess pressure and flow but also pump between reservoirs
Pumping of brine, bromine, vanadium redox with leak-free pumps ensuring zero chance of leakage and avoiding human contact
Pump materials to accommodate brines, empty brine ponds and handle aggressive chemicals
Efficient pump design ensuring low energy consumption, and DC currents